Wayne National Forest
| Wayne National Forest | |
|---|---|
 Welcome Sign for Wayne National Forest | |
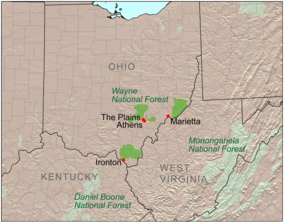 Location of Wayne National Forest | |
| Location | Ohio, United States |
| Coordinates | 39°30′0″N 82°0′0″W / 39.50000°N 82.00000°W |
| Area | 240,101 acres (971.65 km2)[1] |
| Established | December 1992[2] |
| Named for | Anthony Wayne |
| Website | Wayne National Forest |
The Wayne National Forest is located in the Appalachian part of the US state of Ohio, in the Unglaciated Allegheny Plateau. It is the first and only national forest in Ohio. Forest headquarters are located between The Plains and Nelsonville, Ohio, on US Route 33 overlooking the Hocking River.
First referred to as "Ohio National Forest" (unofficially),[3] the Wayne National Forest was later officially named in honor of General Anthony Wayne, an American soldier, officer, statesman, and one of the Founding Fathers of the United States. He served in the American Revolutionary War and was later recalled from civilian life by President George Washington after St. Clair's defeat to command the Legion of the United States in the Northwest Indian War to gain control of the British controlled ceded Northwest Territory, including the region that is now Ohio.[4]
The forest comprises three administrative and purchase units: Athens, Marietta, and Ironton. The Athens and Marietta Units are managed together as the Athens Ranger District, while the Ironton Unit is managed as the Ironton Ranger District. Many of the lands included in the national forest are former coal-mining lands, and much of this land is owned by the federal government without the mineral rights, those having been retained by former owners.
As of September 2018, Wayne National Forest has 244,265 acres (989 km2) in federal ownership within a proclamation boundary of 832,147 acres (3,368 km2).[1]
- The Athens Unit is located in Athens, Hocking, Morgan, Perry, and Vinton Counties, and includes 67,224 acres (272 km²) as of 2002. It features the Wildcat Hollow Trail, a hiking trail just northeast of Burr Oak State Park in Morgan County; the Stone Church Horse Trail in Perry County; the Utah Ridge Recreation Area in Athens County, and the Dorr Run ATV Trails in Hocking County.
- The Marietta Unit is located in Monroe, Noble, and Washington Counties, and includes 63,381 acres (256 km²) as of 2002, with over half of the total being within Washington County.
- The Ironton Unit is located in Gallia, Jackson, Lawrence, and Scioto Counties, and includes 99,049 acres (401 km²) as of 2002, with over two-thirds of the total being within Lawrence County.
The North Country Trail passes through several areas of Wayne, in which it is coincident with the Buckeye Trail and the American Discovery Trail. The area of Ohio included within the national forest is based on late Paleozoic geology, heavy in sandstones and shales, including redbeds, with many coal beds. The topography is typically very rugged, with elevation changes typically in the 200–400-foot range.
History
[edit]The land on which the forest exists and grows was consigned to the United States by the Northwestern Confederacy in 1795 as part of the Treaty of Greenville; it is in the State of Ohio which was named for an indigenous word translating to "Good River."[5][6][7][8]
During the late 18th and 19th century, the forested land was cleared for agricultural and lumbering use, but years of poor timbering and agricultural practices led to severe erosion and poor soil composition. The Wayne National Forest was started as part of a reforestation program. It was established as a National Forest for the public in December 1992.[9]
On April 4, 2024, the Biden Administration proposed that fracking be permitted in the forest, a plan which drew widespread criticism.[10] The administration's Bureau of Land Management announced it would open 40,000 acres (16,000 ha) of the Wayne to fracking for oil and gas. The new proposal, released in late March 2024, is nearly identical to the fracking plan that was blocked in 2020 by a federal judge after conservation groups had challenged it in federal court.[11]
On May 23, 2024, The Wayne National Forest planted a Moon Tree sapling at its Forest Headquarters building in Nelsonville, Ohio, as part of an initiative between NASA and the U.S. Forest Service. The sweetgum sapling was one of fewer than 1,500 seedlings flown thousands of miles beyond the moon aboard the unmanned Orion spacecraft, spending six weeks in space during NASA’s Artemis I mission that had launched on November 16, 2022.[12]
Proposed renaming
[edit]On August 21, 2023, the U.S. Forest Service proposed changing the forest's name to "Buckeye National Forest" after considering other names that included "Ohio National Forest" (its first unofficial name) and "Koteewa National Forest" (Shawnee word for Buckeye).[13] Some supporters of changing the name, including the City Council of Athens in an official letter dated September 5, 2023,[14] prefer "Ohio National Forest," or "Pawpaw National Forest" for the official state native fruit,[15] to be chosen instead of "Buckeye National Forest."[16] The change, if adopted by U.S. Secretary of Agriculture Tom Vilsack of Iowa, would cost $400,000 to implement. The call to change the name was initiated primarily by American Indian tribes who objected to its namesake of Anthony Wayne.[17][18] Opposition to changing the name centers on preserving Wayne's impact to Ohio, critiques of pop history (citing Wayne's complexity), and the violence caused by both tribes and settlers.[19]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b "Land Areas of the National Forest System" (PDF). U.S. Forest Service. January 2012. Retrieved June 30, 2012.
- ^ "History". Wayne National Forest. Archived from the original on November 21, 2001. Retrieved January 19, 2009.
- ^ Vugrincic, Allie (September 5, 2023). "Name change considered for Ohio's Wayne National Forest". Ideastream Public Media. Retrieved November 1, 2024.
- ^ Stockwell, Mary (January 1, 2018). Unlikely General: "Mad" Anthony Wayne and the Battle for America. Yale University Press. p. 211. ISBN 978-0-300-21475-8.
- ^ Bright, William (2004). Native American Placenames of the United States. University of Oklahoma Press. p. 344. ISBN 978-0-8061-3598-4. Retrieved October 29, 2024.
- ^ "Native Ohio". American Indian Studies. Ohio State University. Archived from the original on February 2, 2007. Retrieved February 25, 2007.
Ohio comes from the Seneca (Iroquoian) 'ohiiyo' 'good river'
- ^ "Quick Facts About the State of Ohio". Ohio History Central. Archived from the original on February 8, 2009. Retrieved October 29, 2024.
From Iroquois word meaning 'great river'
- ^ Mithun, Marianne (1999). "Borrowing". The Languages of Native North America. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 311–3. ISBN 978-0-521-29875-9. Archived from the original on July 14, 2023. Retrieved October 29, 2024.
Ohio ('large creek')
- ^ Mangus, Michael; Herman, Jennifer L. (2008). Ohio Encyclopedia. North American Book Dist LLC. p. 570. ISBN 978-1-878592-68-2.
- ^ "Federal plan would open Ohio's national forest to fracking". Center for Biological Diversity. April 4, 2024. Retrieved October 29, 2024.
- ^ "Federal Plan Would Open Ohio's Only National Forest to Fracking". Center for Biological Diversity. Retrieved June 24, 2024.
- ^ "Wayne National Forest plants Moon Tree in Nelsonville that flew on Artemis I mission". Lancaster Eagle-Gazette. Retrieved June 24, 2024.
- ^ Donaldson, Sarah (September 3, 2023). "Why Ohio's only national forest might get a new name". NBC4 WCMH-TV. Retrieved October 29, 2024.
- ^ Walker, Debbie (September 5, 2023). ""Wayne Letter," City Council - Regular Session - September 05, 2023". Athens, OH - Agendas & Minutes. Retrieved November 4, 2024.
- ^ Kraus, Mia (September 19, 2023). "Athens City Council and Mayor Patterson discuss Wayne National Forest and a collaboration with the Ohio Organized Crime Investigation Task Force". The New Political. Retrieved November 4, 2024.
- ^ Vugrincic, Allie (September 5, 2023). "Name change considered for Ohio's Wayne National Forest". Ideastream Public Media. Retrieved November 1, 2024.
- ^ "Wayne National Forest Proposes Changing Name to Buckeye National Forest". U.S. Forest Service. August 21, 2023. Retrieved August 30, 2023.
- ^ Mathis, Carlos (September 5, 2023). "Ohio's 'offensive' national forest name may change". The Hill. Retrieved June 24, 2024.
- ^ Spectrum, Staff (September 4, 2023). "The vigorous debate behind renaming Ohio's Wayne National Forest". Spectrum News. Retrieved October 30, 2024.
External links
[edit]- Wayne National Forest Official Website
- A Forest Returns: The Success Story of Ohio's Only National Forest –- oral history on the beginnings of the Wayne.
- Economic Analysis of the 2006 Wayne National Forest Plan – a critical analysis of future USFS plans for the Wayne
- [1] An oral history on the beginnings of the Wayne.
- National forests of Ohio
- National forests of the Appalachians
- Allegheny Plateau
- Protected areas of Athens County, Ohio
- Protected areas of Hocking County, Ohio
- Protected areas of Vinton County, Ohio
- Protected areas of Perry County, Ohio
- Protected areas of Morgan County, Ohio
- Protected areas of Washington County, Ohio
- Protected areas of Lawrence County, Ohio
- Protected areas of Gallia County, Ohio
- Protected areas of Jackson County, Ohio
- Protected areas of Monroe County, Ohio
- Protected areas of Noble County, Ohio
- Protected areas of Scioto County, Ohio
- 1992 establishments in Ohio
- Protected areas established in 1992
