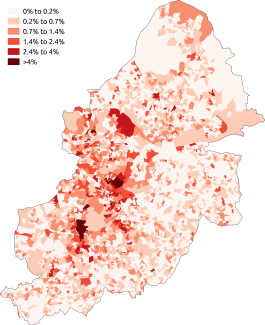
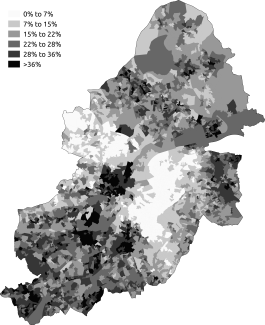
Religion in Birmingham
Religion in Birmingham (2021)[1]
Modern-day Birmingham's cultural diversity is reflected in the wide variety of religious beliefs of its citizens. In the 2021 census, 70% of residents identified themselves as belonging to a particular faith, while 24% stated they had no religion and a further 6% did not answer the question.[2][3]
Distribution
[edit]Early history
[edit]Before Christianity
[edit]Although there were no large Roman settlements in the immediate area of modern-day Birmingham, there was a fort, Metchley Fort near the site of the University of Birmingham, and Icknield Street runs via this site through the western suburbs of the city. The Romano-British population undoubtedly worshipped at pagan temples such as that excavated at Coleshill a few miles outside the modern city boundary, which was possibly dedicated to Minerva or Mars [1], and that identified at Letocetum where Icknield Street crosses Watling Street between Birmingham and Lichfield, also apparently dedicated to Minerva [2].
In the later years of the Roman period, Christianity arrived in the area, although there is little evidence of Christian worship in the immediate Birmingham area at this time. However, when Anglo-Saxon tribes conquered what was to become England in the 5th century, they brought their pagan beliefs with them. Again there is little firm evidence for Anglo-Saxon worship in the area, perhaps because the Anglo-Saxons worshipped in sacred places outdoors rather than in buildings.
The Conversion of Mercia
[edit]Mercia, the Anglo-Saxon Kingdom in which Birmingham was situated, remained pagan for some decades after Saint Augustine had begun the conversion of England. However, under King Penda of Mercia, himself a pagan, Christian missionaries from Lindisfarne were allowed to preach in the kingdom (around 653) and following Penda's death, the rulers of Mercia became Christian and a Diocese of Mercia was created in 656. Part of this became the Diocese of Lichfield in 669 under Saint Chad. (Chad's relics were enshrined at Lichfield Cathedral until the Reformation after which they were kept in hiding until they were transferred to the new Catholic cathedral in Birmingham in 1841 [3]).
The Mediaeval Church
[edit]
Birmingham's original parish church, St Martin in the Bull Ring, has been the site of a church since at least the 12th century, though the earliest parts of the present building date back only to around 1290. Within the modern city boundary, there are a number of other churches which date from the mediaeval period (although many, like St Martin's, were substantially rebuilt in the 19th century). They represent the original mediaeval parishes of the area, which were much larger than the modern parishes of the densely populated city.
In the mediaeval Diocese of Lichfield could be found
- Church of Saints Peter and Paul, Aston in Aston
- St Bartholomew's Church, Edgbaston
- St. Mary's Church, Handsworth
- St. Peter's Church, Harborne
- St Giles' in Sheldon
- Holy Trinity in Sutton Coldfield
In the Diocese of Worcester.
In addition to these parish churches, there was St John's chapel of ease at Deritend founded in 1381 (demolished by 1961), which, though only a short stroll from St Martin's, was in the parish of Aston. Householders in Deritend and Bordesley had the unusual right to elect their own chaplain - a right they continued to enjoy until 1890 when a specific act of parliament was required to regularise the situation [4].
The other main religious organisations in medieval Birmingham were a priory founded in the early 13th century known as the Priory of St Thomas of Canterbury in the area of today's Priory Queensway, and the Guild of the Holy Cross established in 1392, whose guildhall was on New Street.
Christianity
[edit]According to the 2021 census, 34.0% of Birmingham's residents identify themselves as Christian, a huge declined percentage than the England and Wales plurality average of 46.2%.[3] In 2011 census, it was 46.1%, a smaller percentage than the England and Wales average of 59.3%.[2] In 2001 it was 59.1%.
Anglicanism
[edit]Birmingham is the see of the Anglican Diocese of Birmingham which has its cathedral at St. Philip's.
Catholicism
[edit]
Birmingham is the see of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Birmingham which has its cathedral at St. Chad's.
Following the Reformation, Catholicism was effectively outlawed in England, though there remained a number of recusants throughout this period. Several masshouses were established in the district in the 17th century, notably at Oscott around 1679 and in Birmingham itself on what is now called Masshouse Queensway in 1687, although this chapel was burnt down by an anti-Catholic mob the following year. After the process of Catholic Emancipation began in 1778, a Catholic church dedicated to Saint Peter was built on Broad Street in 1786 and Oscott College was founded as a seminary in 1794.
When St. Chad's was begun in 1841 to a design by Augustus Pugin, it became the first Catholic cathedral in England since the Reformation. In the same period, Oscott College moved to a new building, also partly designed by Pugin, at New Oscott, and John Henry Newman, probably the most significant Catholic figure associated with Birmingham, founded the Birmingham Oratory which moved to its present site in Edgbaston in 1852, and its associated Oratory School (1859). When the Catholic hierarchy was restored in 1850, Birmingham was made a diocese and the Catholic population of the town and surrounding district continued to grow throughout this period with a number of churches and religious houses being established.
The growth in Catholic numbers in the 19th century was fuelled partly by Irish immigration, and a mix of anti-popery and xenophobia led to some confrontations in the town, notably the Murphy Riots of 1867.[4] However, there was relatively little strife and Catholics in Birmingham began to be accepted by the establishment of the town. Birmingham became an archdiocese in 1911, and the Catholic population continued to grow along with the city, helped by further waves of immigration, primarily from Ireland, but also including Polish, Italian, Ukraininan and Vietnamese immigrants.
Today the number of Catholics in the archdiocese (which extends beyond Birmingham to take in the rest of the West Midlands, Warwickshire, Worcestershire, Staffordshire and Oxfordshire) has begun to fall from a peak circa 1980.[5] There are many Catholic voluntary aided primary and secondary schools in the city and Newman University in Bartley Green which trains Catholic teachers.

The Orthodox churches
[edit]The Dormition of the Mother of God and St Andrew, Birmingham is a Greek Orthodox cathedral under the jurisdiction of the Patriarchate of Constantinople (Fener, Istanbul), via the Archdiocese of Thyateira and Great Britain (based in Craven Hill, London).
The Church of The Holy Trinity and St Luke is a Greek Orthodox church under the jurisdiction of the Patriarchate of Constantinople (Fener, Istanbul), via the Archdiocese of Thyateira and Great Britain.
There is a Serbian Orthodox church in Bournville, one of the few purpose-built Orthodox churches in the United Kingdom. It is dedicated to the Holy Prince Lazar, who died at the Battle of Kosovo in 1389.
Saints Constantine & Helen Orthodox Church in Erdington is a Greek Old Calendar parish established about fifty years ago. The primary language of the parish community is English.[6]
St. Mary & St. Mark's Coptic Centre, St. Mary & St. Antony's Church and the yet to be constructed cathedral of St. Mary & Archangel Michael are located in the suburbs of Birmingham under the jurisdiction of the Coptic Orthodox Diocese of the Midlands which is led by Bishop Missael. The first Coptic Orthodox Church in Birmingham was St. Mary & St. Antony's which was established in 1985. The city of Birmingham is also where the Diocese is headquartered (at St. Mary & St. Mark's Coptic Centre where Bishop Missael resides).
Other churches
[edit]
There are also other denominations such as Elim Pentecostal Church with ten Churches,[7] New Frontiers Church with 3 churches,[8] Assemblies of God with 12 churches and many more denominations. The Gathering started in Birmingham Christian Centre in 2004 and is now regularly attracting over 1,500 young Christians and non-Christians.[7] The administrative headquarters of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints for the United Kingdom are located in Birmingham[9] There are several Christadelphian meeting halls in the city and The Christadelphian Magazine and Publishing Group is based in Hall Green.
Islam
[edit]
In 2021, 30% of the Birmingham population identified themselves as Muslim. This is significantly higher than the average for England and Wales of 6.5%.[3]
The Muslim community in Birmingham is considered one of the most diverse after London with a wide spectrum of people originally from Africa, Eastern Europe, Southern Europe, Western Asia and other Asian countries. Although the earliest Muslims to arrive in Birmingham and England generally are said to have been from Yemen and the regions of South Asia now known as Bangladesh, it is the Kashmiri community from Mirpur in Pakistan who form the largest group of migrated Muslims. The majority of the Muslims in Birmingham continue to be born abroad as more and more migrants arrive into the city although the number of British-born Muslims and those who convert to the faith are said to be[citation needed] near 50% of the total Muslim population. More recent Muslim settlers hail from Somalia, Kosovo and Algeria and neighbouring nations.
The first mosque in Birmingham was the conversion of a terraced house in Balsall Heath but later a grand project was undertaken by Muslims with the development of the Birmingham Central Mosque in Belgrave Middleway, Highgate, which was conceived in the 1960s and then opened in 1975 to great acclaim as the largest mosque in Western Europe and has since cemented its role as one of Britain's largest and most prominent Islamic centres.
There are currently just over 200 mosques in the city, including purpose built places of worship, converted warehouses, Churches and cinemas as well as former homes, schools and centres. The other prominent mosques and Islamic centres in the city include the Central Jamia Masjid Ghamkol Sharif (located on Poet's Corner in Golden Hillock Road, Sparkhill), Jami Masjid & Islamic Centre in Coventry Road (Coventry Road Mosque), Green Lane Mosque (a former grand library and now modern refurbished Islamic centre and mosque in Green Lane, Small Heath) which is the headquarters of Jamiat Ahl-e-Hadith UK and the 'Amaanah' or Bordesley Centre in Camp Hill run by the Muath Welfare Trust and recently renovated with a generous government grant to continue to provide educational and spiritual services to the large citywide Muslim community. The Bordelsey Centre was established by the city's Yemeni community. Small Heath is home to Wright Street Mosque or the Salafi Masjid which is also an independent primary school.
Birmingham is home to numerous Islamic schools and has many Muslim bookstores and libraries, including the exhibition centres of the Islamic Propagation Centre International (IPCI), one of the country's longest-running Islamic da'wah (proselytisation) organisations. The city also has a Shariah Council run by the Birmingham Mosque Trust.
Daoism
[edit]Birmingham Daoist Community Forum was established in 2010 as the first organisation dedicated to "representing the religion of Daoism in Birmingham".[10]
Humanism
[edit]Humanists and atheists in Birmingham are supported by the Birmingham Humanists, affiliated to Humanists UK. The number of people in Birmingham declaring 'No religion' increased from 19.3% (2011 census) to 24.1% (2021 census). In England and Wales, the number of people declaring 'No religion' has jumped from 25.1% in 2011 to 37.2% in 2021.
Judaism
[edit]
0.1% of Birmingham's residents identify themselves as Jews. This is lower than the average figure for England and Wales of 0.5%.[3]
The existence of a Hebrew street name in the surviving 1344–5 Borough Rentals may indicate the presence of a Jewish community in Birmingham in the 13th century – a period of significant economic growth for the expanding market town. Such a community would however not have survived the Edict of Expulsion of 1290.[11]
Birmingham's developing industry attracted Jewish settlers as early as 1730 and there was already a synagogue in a private house in the area of today's New Street station in 1791, when a purpose-built synagogue was constructed in Hurst Street. The Singers Hill Synagogue in Blucher Street, a Grade II* listed building which is still used for worship today, was built in 1856 [5].
The Jewish population of the city grew in the late 19th century (from 730 in 1851 to 2,360 in 1871) with the influx of Jews from Eastern Europe which led to the founding of two further Orthodox synagogues. In the interwar period, a vibrant Jewish community existed in the area around Holloway Head in the city centre and Jews also settled in the Edgbaston and Moseley areas. This period also saw the founding of the city's Liberal synagogue in Sheepcote Street.
Redevelopment of the Holloway Head area after World War II and a general trend of movement to the suburbs led to Birmingham's Jews becoming more thinly spread across the city. In the same period, however, a voluntary aided school named after King David was established in Moseley, a successor to the city's previous Hebrew school which dated back to the mid-19th century. In recent years, the community has declined in number from around 6,000 in the 1930s to 2,205 in 2011. A number of Jewish families have emigrated to Israel and others are believed to have moved to the larger communities in London and Manchester.
Hinduism
[edit]
According to the 2021 census, 1.9% of Birmingham residents identify themselves as Hindu, above the average figure for England and Wales of 1.7%.[3]
Hindus mainly originate from the Punjab and Gujarat regions of India as well as other regions and countries such as Sri Lanka and Mauritius. Many also came from East Africa.
The first temple in the West Midlands, the Shree Geeta Bhawan temple is located in the Handsworth area of the city on Heathfield Road. Furthermore, one of the largest mandirs in Europe, the Tividale Tirupathy Balaji Temple is located just outside the city in Tividale in the borough of Sandwell.
There are concentrations of Hindus in the Handsworth and Sparkhill sections of the city.
Sikhism
[edit]
2.9% of the population of Birmingham identify themselves as Sikh. The average figure for England and Wales is 0.9%.[3]
The Sikh presence in Birmingham is largely due to immigration in the 1950s and 1960s, although there were Sikhs living in the city before and during World War II. The main organisation for Sikhism in Birmingham is the Council of Sikh Gurdwaras in Birmingham founded in 1989 which represents the city's gurdwaras.
One of the most prominent Sikh events in Birmingham is the annual celebration of Vaisakhi in Handsworth, where many of the city's Sikhs live. The celebrations in 1999 marking the 300th anniversary of the founding of the Khalsa were the largest Vaisakhi celebrations outside of the Punjab.
Buddhism
[edit]
0.4% of the city's residents identified themselves as Buddhist, which is the average for England and Wales of 0.5%.[3] There are over twenty groups of various kinds, and in a variety of buildings, in the city.[12] The most impressive of Birmingham's three Theravada monasteries is the purpose-built Dhamma Talaka Pagoda behind Edgbaston Reservoir, the only such building in traditional Burmese style in the Western hemisphere, which was opened in 1998.
Paganism
[edit]There are a number of Pagan groups active in the Birmingham area. The 2011 census recorded approximately 1,000 Pagans in Birmingham.[13]
Interfaith
[edit]Birmingham's multifaith environment has brought together a number of religious groups and denominations. Birmingham Inter Faiths Council was founded in November 1974; now renamed Birmingham Council of Faiths, it has ten faiths affiliated to it and the city's Lord Mayor acts as its Honorary President in his year of office.[14] It is a charity and its objective is to advance religion and religious education. It is not in favour of atheism.
References
[edit]- ^ "How life has changed in Birmingham: Census 2021". gov.uk.
- ^ a b "2011 Census: KS209EW Religion, local authorities in England and Wales". ons.gov.uk. Retrieved 15 December 2012.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Religion, England and Wales: Census 2021". ons.gov.uk. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
- ^ "Murphy Riots". www.victorianweb.org. Retrieved 24 February 2020.
- ^ "Birmingham (Latin (or Roman) Archdiocese) [Catholic-Hierarchy]". www.catholic-hierarchy.org. Retrieved 24 February 2020.
- ^ "CONTACT US". genuine-orthodoxy. Retrieved 24 February 2020.
- ^ a b "Search". www.elim.org.uk. Retrieved 24 February 2020.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Saints, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day. "Official Website of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints in the United Kingdom and Ireland". www.lds.org.uk. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ "Birmingham Daoist Community Forum to represent local Daoists". Charityzine. Retrieved 16 April 2011.
- ^ Demidowicz, George (2008), Medieval Birmingham: the borough rentals of 1296 and 1344–5, Dugdale Society Occasional papers, vol. 48, Stratford-upon-Avon: The Dugdale Society, in association with the Shakespeare Birthplace Trust, p. 22, ISBN 978-0-85220-090-2
- ^ city council's data base of these can be found here
- ^ "2011 Census: QS210EW Religion (detailed), local authorities in England and Wales". ons.gov.uk. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ "Birmingham Council of Faiths - Welcome". Archived from the original on 5 September 2011.